|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 - -
|
|

|
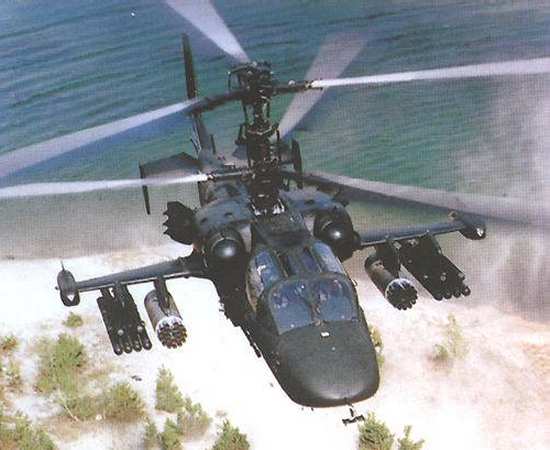
Kamov Ka-50 Black Shark Ka-52 Alligator ASCC codename: Hokum Attack Helicopter |
|
DESCRIPTION:
The Kamov Ka-50 was designed as the world's first single-seat attack helicopter. Although Kamov had originally developed its coaxial rotor scheme (two counter-rotating rotors on the same shaft) for use aboard ships due its compact size, the design team chose to retain the layout for this ground-based helicopter. The Black Shark uses two powerful turbine engines to attain high speed, and the design also features large stub wings to carry a large range of weapons. The wings also help unload the rotors in forward flight to increase manueverability. Survivability is increased through the placement of 160 lb of armor around the cockpit and heat suppressors around the engines to reduce infrared signature. The design is unique since it carries only the pilot, but the Ka-50 relies on other helicopters to locate and designate targets, duties typically performed by a second crew member on other attack helicopters. Russian planners believe this tactic will improve the Ka-50's vulnerability to air defenses since the helicopter is only exposed while releasing its weapons. However, a new more advanced version, the Ka-52, is equipped with side-by-side seating and is intended to lead a group of single-seat Ka-50s in combat. Russia origianlly selected the Ka-50 to go into production at the expense of the rival Mi-28, but both programs have been beset by funding problems since the collapse of the Soviet Union. Ka-50 production was halted in 1994 after only 12 had been built, but it is believed production resumed again from 1996 through at least 1998. Both the Ka-50 and Ka-52 are such advanced and capable attack helicopters that they will likely be successfully exported as well. Countries that have expressed interest in the Ka-50 include India, Algeria, Slovakia, Finland, Singapore, Turkey, Malaysia, Myanmar, South Korea, and Syria.
Data below for Ka-50 |
|
| HISTORY: | |
| First Flight |
(Ka-50) 27 June 1982 (Ka-50N) 5 March 1997 (Ka-52) 25 June 1997 |
|
Service Entry
|
28 August 1995
|
| CREW: |
(Ka-50) one: pilot (Ka-52) two: pilot and weapons officer |
|
ESTIMATED COST:
|
unknown
|
| AIRFOIL SECTIONS: | |
| Rotor Blade Root | unknown |
|
Rotor Blade Tip
|
unknown
|
| DIMENSIONS: | |
| Length |
52.50 ft (16.00 m) rotors turning 49.21 ft (15.00 m) ignoring rotors |
| Rotor Diameter | 47.57 ft (14.50 m) |
| Wingspan | 24.08 ft (7.34 m) |
| Height | 16.17 ft (4.93 m) to top of rotor head |
|
Rotor Disk Area
|
3,555.0 ft² (330.26 m²)
|
| WEIGHTS: | |
| Empty | 16,955 lb (7,690 kg) |
| Normal Takeoff |
(Ka-50) 21,605 lb (9,800 kg) (Ka-52) 22,930 lb (10,400 kg) |
| Max Takeoff | 23,810 lb (10,800 kg) |
| Fuel Capacity |
internal: 495 gal (1,870 L) external: up to 580 gal (2,200 L) in four 145 gal (550 L) underwing tanks |
|
Max Payload
|
6,615 lb (3,000 kg) 3,995 lb (1,810 kg) of expendable weapons |
| PROPULSION: | |
| Powerplant | two Klimov TV3-117VMA turboshafts |
| Thrust |
4,400 hp (3,280 kW)
|
| PERFORMANCE: | |
| Max Level Speed |
at altitude: unknown at sea level: 195 mph (310 km/h) cruise speed: 170 mph (270 km/h) sideways: 45 mph (70 km/h) backwards: 55 mph (90 km/h) dive speed: 215 mph (350 km/h) |
| Maximum Climb Rate | 1,970 ft (600 m) / min |
| Service Ceiling | 18,030 ft (5,500 m) |
|
Hover Ceiling (out of ground effect) |
(Ka-50) 13,125 ft (4,000 m) (Ka-52) 11,810 ft (3,600 m) |
| Range |
typical: 250 nm (460 km) ferry: 625 nm (1,160 km) |
| Endurance | unknown |
| g-Limits |
(Ka-50) +3.5 (Ka-52) +3 |
| ARMAMENT: | |
| Gun | one 2A42 30-mm cannon (500 rds max, 280 rds typical) |
| Stations | 2 stub-wings with 4 hardpoints and 2 wingtip hardpoints |
| Air-to-Air Missile | R-60/AA-8 Aphid, R-73/AA-11 Archer, Igla-V |
| Air-to-Surface Missile | up to 12 AT-9 Ataka or AT-16 Vikhr anti-tank, Kh-25ML/AS-10 Karen anti-radiation, Kh-25MP/AS-12 Kegler |
| Bomb | FAB-250/500, KAB-500Kr |
| Other |
up to four 20-round B-8 80-mm rocket pods, up to four 5-round 122-mm rocket pods, UPK-23-250 gun pod,
GUV-8700 machine gun pod, PLAB weapons dispenser, chaff/flare pods
|
| KNOWN VARIANTS: | |
| Ka-50 'Hokum-A' | Single-seat attack helicopter; 12 built by 1994 |
| Ka-50N | Night attack model with a FLIR/LLTV/laser designator system located in the nose, may also be equipped with a mast-mounted radar |
| Ka-52 'Hokum-B' | Two-seat model equipped for command and control as well as combat reconnaissance |
| Ka-52 trainer | Two-seat trainer model |
| Ka-52 EW |
Electronic warfare model equipped with jamming equipment
|
|
KNOWN COMBAT RECORD:
|
Chechnya (Russia, 2000)
|
|
KNOWN OPERATORS:
|
Russia, Voyenno Vozdushniye Sili (Russian Air Force)
|
|
3-VIEW SCHEMATIC:
Ka-50: 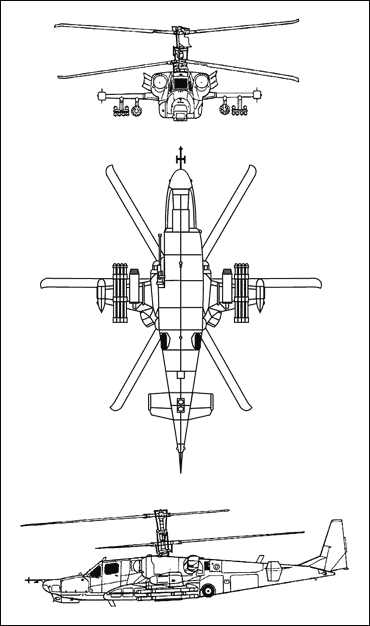
Ka-52: 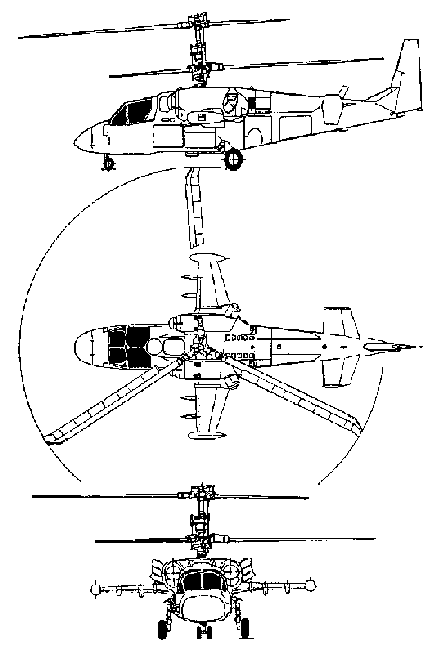
|
|
SOURCES:
|
|


|
Aircraft | Design | Ask Us | Shop | Search |
|
|
| About Us | Contact Us | Copyright © 1997-2023 | |||
|
|
|||