|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 - -
|
|

|
Shenyang J-8, F-8 ASCC codename: Finback Interceptor |
|
DESCRIPTION:
The J-8 was originally developed to meet a Chinese People's Liberation Army Air Force requirement for a fighter superior to the MiG-21. Shenyang met this need with an enlarged twin-engined derivative of the MiG-21. Although based on the MiG-21 and bearing a resemblance to the Mikoyan Gurevich Ye-152A 'Flipper' prototype, the J-8 is a unique Chinese design. The early J-8 and J-8I models were generally similar to each other using the same engines and intake design, but the J-8I incorporated a fire-control system allowing all-weather capability and a number of aerodynamic refinements. However, most of these early aircraft were used for testing and trials purposes only, and production soon shifted to the radically redesigned J-8II. The J-8II 'Finback-B' featured a new forward fuselage making room for a much larger radar, and the centerline inlet used on the earlier models was replaced by side inlets derived from those used on the MiG-23. Several aerodynamic improvements were also made, including addition of a folding ventral strake like that of the MiG-23. Despite these upgrades, the J-8I and J-8II proved to be troubled aircraft that never fully met expectations. China attempted several programs to upgrade the aircraft with Western avionics, but these proved unsuccessful in the wake of the Tienanmen Square incident in 1989. Instead, China and Russia co-developed the J-8IIM (or F-8M), an improved model with new avionics, more powerful engines, and better weapons. China states the J-8IIM offers survivability, high-altitude performance, low-altitude maneuverabilty, and an electronics suite as good or better than early models of the F-16, F-18, and Mirage 2000. Though these claims may be somewhat exaggerated, the aircraft is a low-cost, simple, rugged plane. Export models based on the J-8II have been marketed without success, although some reports indicate that Iran has been interested in the design.
Data below for J-8II |
|
| HISTORY: | |
| First Flight |
(J-8) 5 July 1969 (J-8I) 24 April 1981 (J-8II) 12 June 1984 (J-8IIM) 31 March 1996 |
|
Service Entry
|
1980 (?)
|
| CREW: |
one: pilot
|
|
ESTIMATED COST:
|
unknown
|
| AIRFOIL SECTIONS: | |
| Wing Root | unknown |
|
Wing Tip
|
unknown
|
| DIMENSIONS: | |
| Length | 70.83 ft (21.59 m) |
| Wingspan | 30.58 ft (9.34 m) |
| Height | 17.75 ft (5.41 m) |
| Wing Area | 454.25 ft² (42.20 m²) |
|
Canard Area
|
not applicable
|
| WEIGHTS: | |
| Empty | 21,650 lb (9,820 kg) |
| Normal Takeoff | 31,500 lb (14,300 kg) |
| Max Takeoff | 39,240 lb (17,800 kg) |
| Fuel Capacity |
internal: 8,805 lb (3,995 kg) external: 3,095 lb (1,405 kg) |
|
Max Payload
|
9,920 lb (4,500 kg)
|
| PROPULSION: | |
| Powerplant |
(J-8) two Liyang Wopen-7B afterburning turbojets (J-8II) two Liyang Wopen-13A II afterburning turbojets |
| Thrust |
(J-8) 26,896 lb (119.64 kN) with afterburner (J-8II) 29,630 lb (131.8 kN) with afterburner |
| PERFORMANCE: | |
| Max Level Speed |
at altitude: 1,450 mph (2,340 km/h) at 36,090 ft (11,000 m), Mach 2.2 at sea level: unknown cruise speed: 800 mph (1,300 km/h) |
| Initial Climb Rate | 39,370 ft (12,000 m) / min |
| Service Ceiling | 66,275 ft (20,020 m) |
| Range |
typical: 865 nm (1,600 km) ferry: 1,400 nm (2,600 km) |
| g-Limits |
+4.83
|
| ARMAMENT: | |
| Gun |
(J-8) two 30-mm cannons (J-8I/II) one 23-mm GSh-23 cannon (250 rds) |
| Stations | seven external hardpoints |
| Air-to-Air Missile |
(J-8I/II) up to four PL-2 or up to four PL-7 (J-8IIM) PL-5, PL-8, R-27/AA-10 (J-8D) PL-8, PL-11 |
| Air-to-Surface Missile | none |
| Bomb | 250 kg bombs, 500 kg bombs |
|
Other
|
55-mm rocket pods, 90-mm rocket pods
|
| KNOWN VARIANTS: | |
| J-8 'Finback-A' | Prototype and initial production fighter, saw limited production |
| J-8I 'Finback-A' | Much improved fighter with a new radar in an enlarged intake centerbody giving all-weather capability, twin 30-mm cannons replaced by a single 23-mm cannon, ability to carry rocket pods and the PL-2 AAM, and various aerodynamic improvements; approximately 100 built including upgraded J-8 airframes |
| J-8II 'Finback-B' | Radically modified model with a new solid nose allowing a much more powerful radar to be installed and side intakes borrowed from the MiG-23 feeding more powerful engines |
| F-8II | Export version of the J-8II equipped with uprated engines, a pulse-Doppler radar, and digital avionics; failed to attract any buyers |
| J-8IIM or F-8IIM | Improved J-8II intended for export with improved radar, HUD, INS/GPS navigation system, better weapons, and uprated engines |
| J-8D | Similar to the J-8IIM but with in-flight refueling capability; approximately 30 built by 2000 |
| J-8III or J-8C |
Rumored new build model to be equipped with a canard, fly-by-wire control system, improved radar, and
better engines
|
|
KNOWN COMBAT RECORD:
|
none
|
|
KNOWN OPERATORS:
|
China, Zhongkuo Shenmin Taifang Tsunputai (People's Liberation Army Air Force)
|
|
3-VIEW SCHEMATIC:
J-8: 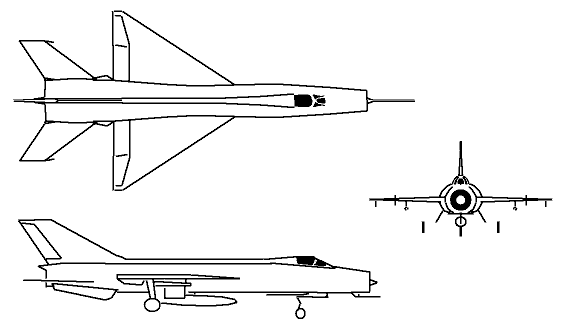
J-8II: 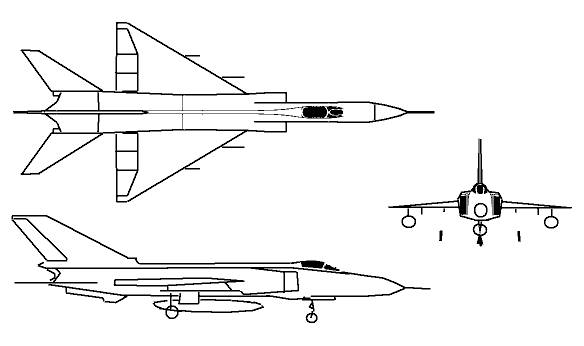
|
|
SOURCES:
|
|


|
Aircraft | Design | Ask Us | Shop | Search |
|
|
| About Us | Contact Us | Copyright © 1997-2023 | |||
|
|
|||